Stock #3 | Jul ’24 | (MSFT)

Understanding $MSFT: A Behemoth of Technology and a Dividend Prince
By Zach Gedal | 30-minute read
Part 1: Company Overview and Philosophy
- Introduction
- Founding and Early History
- Cultural and Ethical Values
- Leadership Philosophy and Style
- Innovation and Adaptability
- Strategic Decision-Making
- Human Capital and Management
- Market Position and Competitive Landscape
- Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Part 2: Dividend Philosophy and Sustainability
- Dividend Tradition and Philosophy
- Dividend Consistency and Culture
- Impact of Corporate Decisions on Dividends
- Stakeholder Value Creation
- Financial Prudence and Allocation
- Economic Moats and Dividend Safety
- Corporate Governance and Dividend Policy
- Long-Term Vision and Dividend Growth
- Qualitative Insights and Future Outlook
Introduction
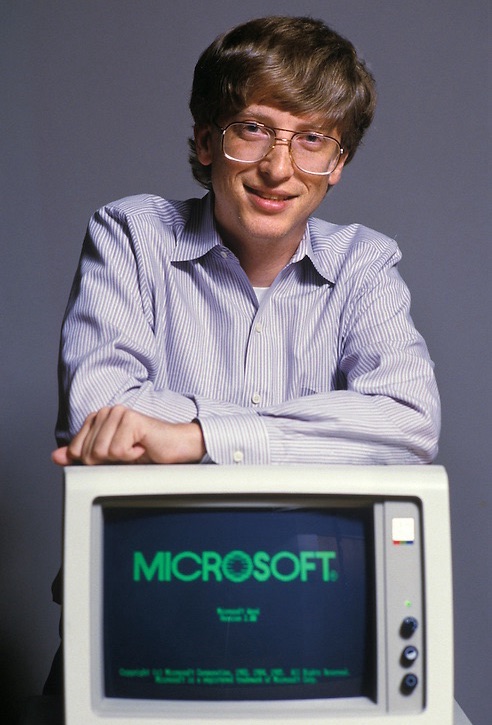

Microsoft Corporation (Ticker: MSFT), a pivotal player in the global technology sector, offers a broad array of software products, cloud solutions, and digital services. Founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen in 1975, Microsoft has established itself as a leader in the IT industry, contributing significantly to the evolution of personal and business computing. The company’s current market strategy and its ability to sustain a strong dividend yield reflect its ongoing commitment to shareholder value and its robust financial health.
Founding and Early History

The journey of Microsoft began in 1975, when Bill Gates and Paul Allen brought to life their vision of a computer on every desk and in every home. Starting with the basic software for the earliest personal computers, Microsoft pioneered the operating system market with MS-DOS followed by the introduction of Windows. These foundational products set the stage for a suite of services that would revolutionize the way the world interacts with technology, laying the groundwork for its expansive cloud and productivity solutions that dominate today.
Inspired by the launch of the first microcomputer, the Altair 8800, Gates and Allen saw an unprecedented opportunity to transform computing with software accessible to the average person. They founded Microsoft with a dream to put a computer on every desk and in every home, a vision that would ultimately redefine the technological landscape.
The company’s inaugural product, a version of BASIC for the Altair, proved to be a hit, marking Microsoft’s entry into the software industry. This success was quickly followed by the development of MS-DOS, a disk operating system commissioned by IBM for its first personal computer. MS-DOS solidified Microsoft’s position in the industry, setting the stage for the launch of Windows in 1985. Windows introduced a graphical user interface (GUI) that simplified computer operation, making it more user-friendly and accessible to a broader audience. These early products were pivotal, laying the foundational stones for Microsoft’s growth into a dominant force in software innovation.
Cultural and Ethical Values

Microsoft’s journey since its founding in 1975 has been deeply influenced by its strong corporate culture and commitment to ethical practices. This is a company that believes firmly in the power of technology to improve lives and solve global challenges—a principle that permeates every aspect of its operations. Under the leadership of Satya Nadella, Microsoft has emphasized a culture of “growth mindset,” a term popularized by psychologist Carol Dweck. This approach encourages an environment where employees are motivated to learn and innovate continuously, rather than merely proving themselves.
Ethics play a central role in Microsoft’s operations, particularly in how it handles data privacy and security—a critical issue for technology companies today. Microsoft has consistently advocated for stronger privacy regulations and has implemented rigorous standards to protect user data. Furthermore, Microsoft’s dedication to corporate social responsibility is reflected in its extensive sustainability efforts. The company has committed to becoming carbon negative by 2030 and to eliminate its historical carbon emissions by 2050, underscoring its commitment to environmental stewardship.
These cultural and ethical commitments have significant implications for Microsoft’s financial health and its attractiveness as a dividend-paying stock. A strong ethical foundation attracts and retains talent, enhances customer loyalty, and mitigates regulatory risks, all of which contribute to steady financial performance. Microsoft’s robust dividend history, characterized by consistent payouts and periodic increases, can be seen as a reflection of its strong cash flow, stable earnings, and the ethical manner in which it conducts business. This ethical resilience and cultural strength make Microsoft a compelling consideration for your dividend-focused investment portfolio, promising not just returns but also aligning with a broader mission of positive global impact.
Connections with Jeffrey Epstein
Bill Gates, co-founder of Microsoft, has been scrutinized for his past association with convicted sex offender Jeffrey Epstein. These connections surfaced after Epstein’s arrest and death in 2019, with Gates admitting that meeting Epstein was a mistake. Although Gates stepped away from his daily roles at Microsoft in 2008 and left the board in 2020, his identity remains closely linked with Microsoft. This association has brought negative attention and could potentially harm Microsoft’s image. Public perception and trust in Microsoft might suffer due to these controversies, especially among stakeholders sensitive to ethical conduct. This situation underscores the impact that the personal actions of corporate leaders can have on their companies’ reputations, potentially influencing investor sentiment and stakeholder trust in the longer term.
However, it’s critical to address that even a firm as robust as Microsoft is not immune to ethical scrutiny. The controversies surrounding Bill Gates’ connections with Jeffrey Epstein have raised questions about leadership judgment and corporate oversight. These revelations necessitate a reevaluation of Microsoft’s ethical commitments and transparency, highlighting the importance of maintaining a culture that truly reflects its publicly stated values. This continuous commitment to ethical rigor not only reassures stakeholders but also solidifies Microsoft’s standing as a leader in both technology and corporate responsibility, essential for long-term investor confidence and market sustainability.
Leadership Philosophy and Style

Microsoft’s leadership philosophy and style have been pivotal in shaping its corporate culture and strategic direction, particularly under the guidance of its current CEO, Satya Nadella. Since taking the helm in 2014, Nadella has significantly transformed the company’s approach, fostering a culture of inclusivity, innovation, and continuous learning. Nadella’s leadership is heavily influenced by his belief in the growth mindset, a concept he popularized within the company based on the work of psychologist Carol Dweck. This philosophy encourages employees at all levels to embrace challenges, learn from criticism, and celebrate the successes of others. It’s a stark shift from the more competitive environment under previous leadership regimes, promoting cooperation and team learning over individual achievement.
Ethical leadership is another cornerstone of Nadella’s approach. He has consistently emphasized the importance of maintaining integrity and accountability, especially as Microsoft navigates complex issues like privacy, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence ethics. This focus on ethical decision-making is not only about doing right by Microsoft’s customers and partners but is also seen as essential to long-term business sustainability. Under Nadella, Microsoft has also embraced a more flexible and responsive leadership style. He has de-emphasized hierarchical decision-making and given more autonomy to frontline teams. This decentralization allows for quicker adaptation to technology shifts and market demands, a critical factor in the tech industry’s fast-paced environment.
Moreover, Nadella’s emphasis on empathy as a leadership trait has redefined interpersonal dynamics within Microsoft. He advocates for understanding the user’s experience and walking in the shoes of both customers and employees to better meet their needs. This empathetic approach has helped Microsoft improve its products and services, enhancing customer satisfaction and employee morale. The impact of this leadership style is evident in Microsoft’s continued innovation, robust financial performance, and its ability to attract and retain top talent. These factors are crucial in supporting the company’s ability to continue paying dividends, making it a reliable pick for income-focused investors. Nadella’s leadership not only drives Microsoft’s current success but also secures its future by cultivating a resilient and adaptable corporate culture.
Innovation and Adaptability

Microsoft’s legacy of innovation is not just a reflection of its past successes but a driving force for its future. The company’s ability to adapt and innovate has been central to its growth strategy, helping it stay relevant as technology evolves at a breakneck pace. This adaptability stems from its foundational days when it quickly moved from BASIC interpreters to dominating the PC operating system market with MS-DOS and subsequently Windows.
Under Satya Nadella’s leadership, Microsoft has embraced a philosophy of “tech intensity” which Nadella describes as “tech adoption combined with tech capability” (Nadella, 2019). This approach means not only using the latest technologies but also building proprietary technology to maintain a competitive edge. This strategy has seen Microsoft making significant advances in cloud computing with Azure, which has emerged as a formidable competitor to Amazon’s AWS.
Moreover, Microsoft’s innovation extends beyond products to its organizational practices. The company has adopted a more open approach to collaboration, breaking down internal silos and promoting synergy across departments. This has fostered an environment where ideas can flourish from any level within the organization, driving innovation. For instance, Microsoft’s decision to open-source its .NET framework and collaborate with competitors like Red Hat speaks to a broader strategy of strengthening ecosystems where Microsoft products can become more entrenched and indispensable.
Microsoft also adapts by continually reassessing its product lineup and market strategy. An example of this is the shift from focusing primarily on software licensing to embracing a subscription model with Office 365, enhancing customer retention and stabilizing revenue flows. This adaptability not only secures Microsoft’s position in software and cloud domains but also strengthens its hand in emerging areas like AI and quantum computing.
This combination of foresight in technological adoption, cultural flexibility within corporate structures, and strategic pivots in business models underscores Microsoft’s robust framework for sustained innovation and adaptability. These attributes make Microsoft a compelling case study in how enduring companies can continually reinvent themselves in the face of rapid technological change, securing their place as both industry leaders and reliable dividend payers.
Subscription Services Shift
Microsoft’s strategic shift to subscription-based services such as Office 365 and Microsoft 365 marks a significant transformation in its business model, showcasing its adaptability and innovative capabilities. This move to recurring subscription services provides a more predictable and stable revenue stream, which is particularly valuable during economic downturns as it mitigates the impact of decreased one-time sales.
The subscription model also enhances customer retention by fostering continuous relationships with users. Regular updates and the addition of new features help maintain customer engagement, ensuring a long-term customer base that proves more cost-effective than constantly acquiring new users. This ongoing relationship not only secures a consistent cash flow but also enables Microsoft to plan and invest confidently in future projects and innovations, maintaining its position at the forefront of technology.
For investors, the predictable revenue generated from subscriptions makes Microsoft an attractive investment, particularly in terms of dividend reliability. In periods of economic uncertainty, the company’s steady cash flow supports its ability to maintain or increase dividend payouts, thereby enhancing shareholder value. Furthermore, the subscription model allows Microsoft to respond more agilely to market demands, using continuous feedback from users to drive quick adaptations and improve product offerings. Overall, this strategic pivot not only underlines Microsoft’s commitment to continuous innovation but also strengthens its financial resilience and competitive edge in the rapidly evolving tech industry.
Strategic Decision-Making

Microsoft’s approach to human capital and management underscores its reputation as a leading technology company committed to fostering a productive and innovative workforce. Recognizing that its success hinges on the talents and efforts of its employees, Microsoft has implemented various strategies to attract, develop, and retain top talent across the globe.
The company’s human capital strategy is deeply intertwined with its cultural shift towards a growth mindset, as advocated by CEO Satya Nadella. This philosophy encourages employees to learn continuously, embrace challenges, and work collaboratively. Microsoft supports this culture through substantial investments in employee development programs, including continuous learning opportunities and leadership training tailored to foster innovation and agility within its ranks. This focus on personal and professional growth helps maintain a high level of employee engagement and motivation.
Furthermore, Microsoft’s management practices reflect a commitment to diversity and inclusivity, understanding that diverse teams are more innovative and perform better. The company has been proactive in its efforts to increase diversity at all levels of the organization, from entry-level positions to senior management and board representation. These initiatives are complemented by robust support systems, such as mentorship programs, networking groups, and inclusive hiring practices, which not only enhance workforce diversity but also strengthen Microsoft’s competitive edge in the technology sector. By prioritizing human capital, Microsoft ensures a sustainable and innovative future, leveraging a well-managed and motivated workforce to drive continued success and growth.
Azure Cloud Services
Azure is a cornerstone in Microsoft’s comprehensive suite of technology offerings, delivering scalable and flexible cloud solutions that cater to a wide range of computing needs. As one of the leading platforms in the cloud industry, Azure’s growth is crucial to Microsoft’s strategy, particularly as it competes with other major providers like AWS and Google Cloud. To maintain and expand its market share, Microsoft is committed to continuously innovating within Azure. This includes deploying advanced cloud technologies, enhancing security features, and expanding global data center infrastructure. Additionally, Microsoft aims to differentiate Azure by integrating it with other services and emphasizing its hybrid capabilities, which allow customers to seamlessly bridge their on-premises infrastructure with the cloud. These efforts are designed to meet the evolving needs of businesses and organizations around the world, ensuring that Azure remains at the forefront of cloud technology solutions.
Human Capital and Management

Microsoft’s approach to human capital and management underscores its reputation as a leading technology company committed to fostering a productive and innovative workforce. Recognizing that its success hinges on the talents and efforts of its employees, Microsoft has implemented various strategies to attract, develop, and retain top talent across the globe.
The company’s human capital strategy is deeply intertwined with its cultural shift towards a growth mindset, as advocated by CEO Satya Nadella. This philosophy encourages employees to learn continuously, embrace challenges, and work collaboratively. Microsoft supports this culture through substantial investments in employee development programs, including continuous learning opportunities and leadership training tailored to foster innovation and agility within its ranks. This focus on personal and professional growth helps maintain a high level of employee engagement and motivation.
Furthermore, Microsoft’s management practices reflect a commitment to diversity and inclusivity, understanding that diverse teams are more innovative and perform better. The company has been proactive in its efforts to increase diversity at all levels of the organization, from entry-level positions to senior management and board representation. These initiatives are complemented by robust support systems, such as mentorship programs, networking groups, and inclusive hiring practices, which not only enhance workforce diversity but also strengthen Microsoft’s competitive edge in the technology sector. By prioritizing human capital, Microsoft ensures a sustainable and innovative future, leveraging a well-managed and motivated workforce to drive continued success and growth.
Strategic Acquisitions and Growth
Building on its robust human capital and management strategies, Microsoft has also leveraged strategic acquisitions to sustain growth and diversify its product offerings. A prime example of this approach is the company’s planned $68.7 billion acquisition of Activision Blizzard, one of the largest deals in the tech industry and a significant move for Microsoft’s gaming segment.
This acquisition is poised to substantially enhance Microsoft’s gaming portfolio by adding some of the world’s most popular video games, including iconic franchises such as Call of Duty, World of Warcraft, and Overwatch. These titles not only boast massive, dedicated user bases but also offer recurring revenue through their subscription-based and in-game purchase models. Integrating these successful franchises with Microsoft’s existing gaming ecosystem, which includes Xbox and the Game Pass subscription service, could lead to increased user engagement and higher subscription numbers. The deal, therefore, has the potential to transform Microsoft into an unrivaled leader in the gaming industry, both in terms of revenue and influence.
Moreover, the acquisition of Activision Blizzard aligns well with Microsoft’s strategic emphasis on cloud computing and mobile platforms. By harnessing its cloud technology, Microsoft can further enhance the gaming experience through more seamless gameplay, improved graphics, and reduced latency. This integration can extend even to mobile gaming, a rapidly growing sector that Activision Blizzard has already tapped into with significant success. The synergy between Microsoft’s technological prowess and Activision Blizzard’s content could thus create a more immersive and accessible gaming experience across multiple platforms.
The potential benefits extend beyond just technological and product synergies. Strategically, this acquisition also positions Microsoft to leverage a broader entertainment ecosystem that can integrate gaming with other forms of digital entertainment, potentially including virtual and augmented reality offerings. This could open new revenue streams and market opportunities, particularly in the evolving landscape of interactive and virtual entertainment.
Market Position and Competitive Landscape

Microsoft occupies a commanding position within the global technology sector, renowned for its extensive suite of products that include software solutions, cloud services, and hardware. Its broad range of offerings such as Windows, Microsoft Office, and Azure cloud services have solidified its status as a staple in both personal and enterprise computing environments. This diversity not only enables Microsoft to tap into multiple revenue streams but also to build a robust and loyal customer base across various market segments.
In terms of competition, Microsoft faces stiff challenges from other tech giants such as Amazon, Google, and Apple. Each of these companies competes with Microsoft in key areas: Amazon in cloud computing services with AWS, Google in productivity software and cloud services, and Apple in consumer electronics and operating systems. Despite this intense competitive environment, Microsoft has managed to maintain its leadership through strategic innovation and customer-centric product development. Its ability to integrate and synergize its products across its ecosystem enhances user experience and creates barriers for customer churn.
Furthermore, Microsoft has adeptly navigated the shifting technological landscape by investing in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and quantum computing. These investments not only prepare Microsoft to lead in future tech trends but also reinforce its current products with advanced capabilities, keeping them competitive and relevant. The company’s strategic acquisitions, such as LinkedIn and GitHub, have also expanded its reach and fortified its position in the technology market, enabling it to offer more comprehensive solutions that meet a wider array of customer needs. Through these concerted efforts, Microsoft continues to assert its dominance in the technology sector, ensuring it remains at the forefront of innovation and market relevance.
Windows Operating System
Expanding on Microsoft’s robust market position, the Windows Operating System remains a critical component of its success. As the backbone of personal computing, Windows continues to generate substantial revenue from Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) who integrate the OS into their hardware products. Despite its success, Microsoft faces challenges in a declining PC market, driven by shifting consumer preferences towards mobile devices and alternative computing platforms. To counteract these trends, Microsoft introduced Windows 11, which boasts a host of new features designed to enhance user experience and increase productivity. Innovations such as a streamlined new design, improved performance features, and better integration with cloud and mobile services are aimed at keeping the OS relevant and appealing in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Moreover, the rise of alternative platforms has prompted Microsoft to push the boundaries of what Windows can offer. Integration with Microsoft’s cloud services, enhanced security measures, and cross-platform capabilities are strategic moves to maintain Windows as a preferred choice for both personal and enterprise computing. By adapting to market needs and leveraging its extensive ecosystem, Microsoft not only sustains its relevance but also sets new standards in the OS market.
Investor Perspectives and Strategic Decisions
Turning to investor perspectives, Microsoft’s strategic decisions and market behavior have always been of significant interest to the investment community. Notable investors like Warren Buffett have historically shown a cautious approach to investing in tech giants like Microsoft. Buffett’s decisions are influenced by his investment philosophy, which prioritizes long-term value, understandable business models, and strong ethical management practices. His limited engagement with Microsoft has often been attributed to these factors, along with potential conflicts of interest and the inherent volatility and competitiveness of the tech sector.
These investor sentiments underscore a broader caution among traditional investors towards rapidly changing tech companies. However, understanding these perspectives provides valuable insights into what constitutes perceived risks and opportunities in the tech industry. For Microsoft, addressing these investor concerns through transparent ethical practices, stable financial management, and clear communication about strategic decisions remains crucial. This approach not only aligns with investor expectations but also bolsters Microsoft’s reputation as a leader committed to sustainable growth and innovation in the technology sector.
Warren Buffett
Warren Buffett’s relationship with Microsoft extends beyond mere investment analysis to encompass personal dimensions, particularly his long-standing friendship with Bill Gates. Despite this close relationship, Buffett has historically avoided significant investment in Microsoft. His rationale is rooted primarily in the principles of conflict of interest and ethical investment strategies. Buffett has often cited his desire to avoid any appearance of insider trading or gaining an unfair advantage through his proximity to Gates, who co-founded Microsoft and served as its CEO for many years.
This cautious approach is also informed by Buffett’s investment philosophy, which emphasizes understanding a company’s business deeply. While he is well-acquainted with Gates, Buffett has mentioned in various interviews that the rapidly changing nature of the technology sector and his limited understanding of tech business specifics have made him hesitant to invest heavily. This is indicative of a broader strategy where Buffett avoids sectors where he perceives his grasp as insufficient for informed investing.
Furthermore, the friendly rivalry between Gates and Buffett has been well-publicized, adding another layer to why Buffett might steer clear of a substantial Microsoft investment. Both figures have often engaged in discussions and playful competitions that highlight their distinct approaches to business and philanthropy, yet maintaining a mutual respect for each other’s expertise and achievements.
Buffett’s limited investment in Microsoft, therefore, is not just a reflection of his investment strategy but also an indication of his strict adherence to ethical investing standards. He aims to prevent any potential conflicts that could arise from his personal connections, thereby maintaining the integrity of his investment decisions. This stance offers insights into how personal relationships and ethical considerations can influence even the most seasoned investors, highlighting the complex interplay between personal connections and professional investment decisions in the world of finance.
Risks and Mitigation Strategies

Microsoft, like any global technology giant, faces a range of risks that could potentially affect its operations and market position. These include technological obsolescence, regulatory challenges, cybersecurity threats, and competitive pressures. However, Microsoft has implemented robust mitigation strategies to address these risks effectively.
Technological Obsolescence: The rapid pace of technological innovation means that products can quickly become outdated. Microsoft counters this risk by maintaining a strong commitment to research and development. This commitment allows the company to stay at the cutting edge of technology, continually updating its offerings and pioneering new products in areas like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Regulatory Challenges: As a major player in the global market, Microsoft often faces regulatory scrutiny in areas such as data privacy, antitrust issues, and cross-border data flows. To mitigate these risks, Microsoft actively engages with policymakers and regulatory bodies around the world to ensure compliance and to shape future regulations in ways that will not unduly hinder its business operations. Additionally, the company invests in comprehensive data protection measures to safeguard user data, thereby aligning with global privacy standards like GDPR.
Cybersecurity Threats: Cyber threats are a significant risk for a company that manages vast amounts of sensitive data. Microsoft addresses this challenge by investing heavily in cybersecurity, both as a feature of its products and as a core aspect of its internal IT infrastructure. The company also offers a suite of security products and services, enhancing its value proposition and creating an additional revenue stream.
Competitive Pressures: The technology sector is highly competitive, with several players constantly vying for market share. Microsoft’s strategy to mitigate this risk includes diversification of its product portfolio and continuous innovation. Moreover, Microsoft builds strong customer relationships through excellent service and support, and by providing integrated solutions that increase customer dependency on its ecosystem.
Regulatory Challenges
Microsoft’s strategic maneuver to acquire Activision Blizzard has come under significant scrutiny from federal regulators, particularly the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). The FTC’s concerns likely center around potential monopolistic tendencies that could arise from such a massive consolidation in the gaming industry. This court hearing is a pivotal moment for Microsoft, as it could set precedents for future tech acquisitions.
The regulatory hurdles present a complex challenge for Microsoft, requiring a nuanced approach to demonstrate that the acquisition would not harm competition but rather foster innovation and consumer benefits. Microsoft’s strategy to navigate these waters includes comprehensive legal arguments, economic impact assessments, and possibly concessions that assure the market remains competitive. The outcome of this hearing could influence Microsoft’s future acquisition strategy and its approach to regulatory compliance. Proactively engaging with regulatory bodies and possibly adjusting the scale or terms of the acquisition could be necessary steps to mitigate these challenges.
Reputational Risks and Management Response
In addition to regulatory challenges, Microsoft must manage its reputational risks, which have been highlighted by past controversies and failed acquisitions. One notable aspect of Microsoft’s strategy to mitigate these risks includes enhancing its corporate governance and transparency. The company has increasingly focused on being upfront about its business practices, decision-making processes, and handling of data privacy concerns.
Furthermore, Microsoft has implemented rigorous compliance programs and regular audits to ensure ethical practices across all levels of the organization. The company also invests in corporate social responsibility initiatives that align with its business objectives, thereby improving public perception and trust. When controversies do arise, Microsoft has shown a proactive approach in addressing them promptly, often going beyond regulatory requirements to rectify issues and prevent future occurrences.
By bolstering its governance structures and maintaining high standards of transparency, Microsoft aims to not only comply with global regulations but also to build and sustain trust with its stakeholders, thereby safeguarding its reputation in a competitive and fast-evolving technological landscape.
Recent Outage at CrowdStrike and Implications for Microsoft
The recent outage at CrowdStrike, a cybersecurity firm, has raised pertinent questions about the resilience and reliability of cloud-based security solutions—a field in which Microsoft is also deeply invested. While Microsoft is not directly involved with this specific incident, the occurrence highlights a critical vulnerability in the cybersecurity infrastructure that could have implications for all major players in the technology sector, including Microsoft.
For Microsoft, the CrowdStrike outage serves as a cautionary tale, emphasizing the importance of robust system architectures and the potential reputational risks associated with service disruptions. Microsoft, leveraging its Azure cloud platform, offers similar cybersecurity services and solutions, making it imperative for the company to reassess and reinforce its own systems to prevent similar incidents.
In response to such industry-wide challenges, Microsoft could enhance its competitive edge by investing further in advanced predictive analytics to foresee potential system failures, improving its incident response strategies, and increasing transparency with clients about how data is protected and how risks are mitigated. Moreover, Microsoft might consider engaging in more rigorous stress testing of its services and conducting regular security audits to ensure the integrity and reliability of its systems.
By taking proactive measures and learning from the challenges faced by other companies like CrowdStrike, Microsoft can not only prevent similar incidents but also strengthen trust in its products and services, ultimately enhancing its market position and customer loyalty in the competitive tech landscape.
Part 2: Dividend Philosophy and Sustainability
Dividend Tradition and Philosophy

Microsoft’s dividend strategy reflects a commitment to delivering consistent shareholder returns while supporting strategic growth opportunities. Starting its dividends in 2003, Microsoft has established a pattern of predictable increases, emphasizing strong cash flow and management’s confidence in sustained profitability.
The graph illustrates Microsoft’s stable dividend history, marked by a steady increase over the years. This trend highlights the company’s ability to enhance shareholder value through careful financial management and robust earnings. Supported by a solid business model that generates significant free cash flow, Microsoft manages to fund dividends comfortably while investing in key areas such as cloud computing and AI.
Microsoft’s approach balances rewarding shareholders and maintaining financial flexibility, ensuring dividends are sustainable over the long term without compromising strategic growth, thereby reinforcing its status as a reliable dividend stock.
Dividend Consistency and Culture

Microsoft’s dividend policy showcases a strong commitment to consistent shareholder returns and financial resilience. Since initiating dividends in 2003, Microsoft has increased its dividend payments almost annually, underpinning a culture that values stable and predictable shareholder returns. This steady increase across the years is a testament to Microsoft’s robust financial health and disciplined approach to capital management.
The consistent upward trend in Microsoft’s dividends reflects its operational success and strategic financial planning. Each dividend increase is supported by the company’s solid earnings and cash flow, which allows for reinvestment in strategic growth areas while also rewarding shareholders. Such reliability in dividend payments not only fosters investor trust but also reinforces Microsoft’s reputation as a secure investment within the volatile technology sector.
This ongoing commitment to increasing dividends highlights Microsoft’s confidence in its business model and future prospects. It underscores the company’s identity as a mature, reliable, and investor-friendly entity, committed to long-term value creation and financial stability.
Impact of Strategic Decisions on Dividends
Microsoft’s ambitious target of reaching $500 billion in annual revenue by 2030 has significant implications for its dividend policy and shareholder returns. Such a growth trajectory suggests a deep confidence in the company’s core business sectors, including cloud computing, productivity software, and gaming platforms, all bolstered by strategic acquisitions and technological innovation. Achieving this goal would likely provide Microsoft with an expanded cash flow capacity, enabling more robust dividend payouts and potentially increasing the frequency and volume of share buybacks.
This commitment to aggressive revenue targets reflects a broader strategy to not only grow in scale but to enhance the stability and predictability of returns to shareholders. For investors, consistent dividend growth is often seen as a signal of a company’s financial health and management’s confidence in future cash flows. Thus, reaching these revenue goals could reinforce investor perception of Microsoft as a stable dividend-paying stock, attractive for both growth and income-focused portfolios.
Moreover, as Microsoft pushes towards this revenue milestone, it will need to continue innovating and possibly diversify its income streams further, ensuring that its growth is sustainable over the long term. This might involve deeper penetration into emerging markets, expansion of cloud services, or new product developments, all of which could further solidify its market position and support an aggressive dividend policy.
The potential increase in dividend payouts and share buybacks as a result of reaching a $500 billion revenue goal would not only reward shareholders but also demonstrate Microsoft’s ability to generate and effectively allocate substantial financial resources. This approach aligns with a dividend policy that supports shareholder value creation through both capital appreciation and income generation, making Microsoft a cornerstone investment in dividend growth portfolios.
In summary, Microsoft’s strategy to significantly increase its revenue by 2030 directly supports a culture of dividend consistency, underlining its role as a reliable steward of investor capital with a clear focus on long-term value creation.
Impact of Corporate Decisions on Dividends:

Microsoft’s strategic decisions have significantly shaped its dividend policies. Its foray into cloud computing with Azure and strategic acquisitions like LinkedIn have bolstered revenues, thereby supporting robust dividend payouts. The integration of these services has not only expanded Microsoft’s market but also stabilized its cash flows, facilitating consistent dividend growth.
The company’s financial strategies, focusing on long-term profitability, have maintained a stable financial base, enabling steady dividend increases. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of dividends over several periods stands testament to this prudent financial management. Microsoft’s adaptability in shifting towards high-growth areas like AI and cloud services has further secured its competitive market position and financial strength—key for sustaining dividends.
Through these deliberate corporate actions, Microsoft has managed to balance growth investments with rewarding shareholders, demonstrating a commitment to both innovation and shareholder returns.
Stakeholder Value Creation:

Financial Prudence and Allocation:
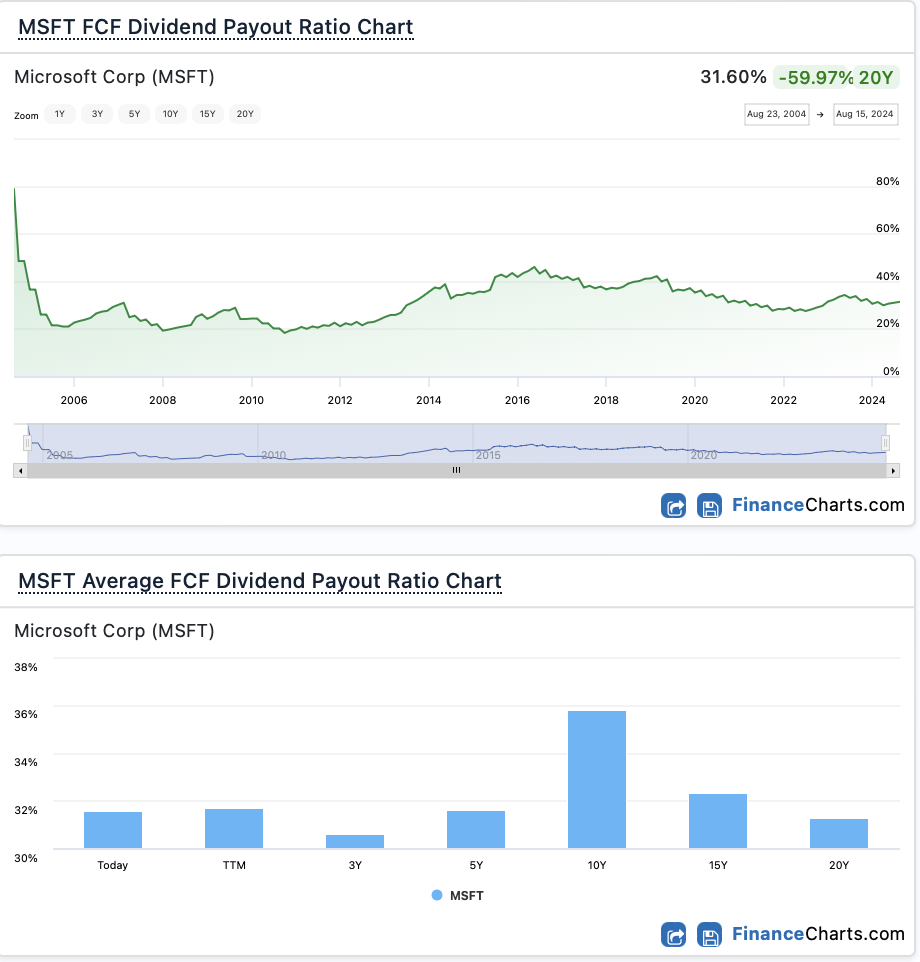
Discuss the company’s financial management and capital allocation.
Economic Moats and Dividend Safety:
Explore the economic moats that protect the company’s dividends.
Corporate Governance and Dividend Policy:
Analyze the governance structures impacting dividends.
Long-Term Vision and Dividend Growth:
Discuss how the company’s long-term strategy supports dividend growth.
Qualitative Insights and Future Outlook:
Conclusion
Synthesis and Strategic Insights
As we integrate Microsoft into our investment portfolio, replacing HFBL for the month of July, we recognize its significant potential for both growth and dividends. Known for its robust financial performance and consistent dividend payouts, Microsoft represents a strategic asset that aligns with our goals of capital appreciation and reliable income generation.
This transition not only reflects our adaptive investment strategy but also our commitment to providing our followers with high-value opportunities in the evolving tech sector. We look forward to exploring Microsoft’s contributions to technology and dividends in upcoming discussions and portfolio updates.
Stay tuned for more detailed insights into Microsoft’s impact on the tech world and our investment strategy in future posts.
Warm regards,
Zachary Gedal
